How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand, opening doors to breathtaking aerial photography, innovative surveying techniques, and exciting recreational pursuits. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental components and regulations to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and maintenance procedures. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and enjoy the many benefits that drone technology offers.
From pre-flight checklists and legal considerations to navigating complex flight controls and troubleshooting potential issues, we cover all aspects of drone operation. We will explore different drone models and their capabilities, providing practical tips and advice to ensure both safe and successful flights. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive guide provides a clear and accessible path to becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as pre-flight checks and maneuvering, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects, including advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to enhance your skills. Mastering these fundamentals will allow you to confidently and safely operate your drone.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. Failure to do so can lead to accidents, fines, and legal repercussions. This section details crucial safety procedures and legal requirements.
Drone Regulations by Location
Drone laws vary significantly depending on location. National parks often have strict regulations, sometimes prohibiting drone flights altogether, while urban areas may have restrictions on flight altitudes and specific no-fly zones near airports or sensitive infrastructure. Always check with the relevant authorities (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) for specific rules in your area before flying.
Registration of your drone might also be required.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation demands a systematic approach, encompassing pre-flight checks, in-flight awareness, and post-flight maintenance. This minimizes risks and ensures the longevity of your equipment.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A thorough pre-flight inspection is essential for safe operation. This checklist helps ensure all systems are functioning correctly before takeoff.
- Battery charge level
- Propeller condition (for damage or cracks)
- Gimbal functionality
- Camera settings
- GPS signal strength
- Remote controller connection
- Visual inspection of the drone body for any damage
Drone Safety Features Comparison
Different drones offer varying safety features. Understanding their importance allows for informed purchasing decisions and safer operation.
| Safety Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. | Crucial for preventing loss in case of signal loss or low battery. |
| GPS | Provides location data for precise navigation and RTH. | Essential for accurate flight and safe operation. |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Detects and avoids obstacles during flight. | Reduces the risk of collisions. |
| Geofencing | Limits the drone’s flight range to a predefined area. | Prevents unauthorized flights and ensures safety. |
Understanding Drone Components and Functions
A drone’s functionality stems from the interplay of its various components. Understanding these components and their interactions is crucial for both safe and effective operation.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in its operation.
- Propellers: Generate thrust for flight.
- Motors: Drive the propellers.
- Battery: Powers the entire system.
- Flight Controller: Processes sensor data and controls the motors.
- Camera: Captures images and videos.
- GPS Module: Provides location and navigation data.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures acceleration and rotation.
Drone Internal Workings Diagram, How to operate a drone
Imagine a diagram showing a cross-section of a drone. The central component is the flight controller, a small circuit board connected to the motors via Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs). The battery is connected to the flight controller, supplying power. The GPS module sits near the flight controller, providing location information. The camera is mounted on a gimbal (a stabilized platform) to minimize image shake.
All these components are interconnected and communicate with each other through the flight controller.
Drone Camera Types and Capabilities
Drone cameras vary significantly in resolution, sensor size, and features. Understanding these differences helps in selecting a camera appropriate for specific needs.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
- Standard Cameras: Offer good image quality for everyday use.
- High-Resolution Cameras: Capture detailed images and videos.
- Thermal Cameras: Detect heat signatures, useful for search and rescue operations.
- RGB Cameras: Capture standard color images.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Procedures
Proper pre-flight preparation is paramount to a safe and successful drone flight. This section details the essential steps involved.
Charging and Connecting the Battery
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Ensure the battery is fully charged before each flight and avoid overcharging.
Calibrating Drone Sensors and Gyroscopes
Calibration ensures accurate readings from the drone’s sensors, leading to stable and predictable flight. Most drones have built-in calibration procedures accessible through the drone’s app or remote control.
Flight Planning
Planning a drone flight involves considering several factors to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
- Choose a suitable location, avoiding restricted airspace.
- Check weather conditions – avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Plan your flight path and ensure you have a clear line of sight.
- Notify relevant authorities if necessary.
Essential Drone Accessories and Tools
Having the right tools and accessories can significantly enhance the drone operation experience and ensure safe operation.
- Extra batteries
- Propeller guards
- Carrying case
- Screwdrivers
- Cleaning cloth
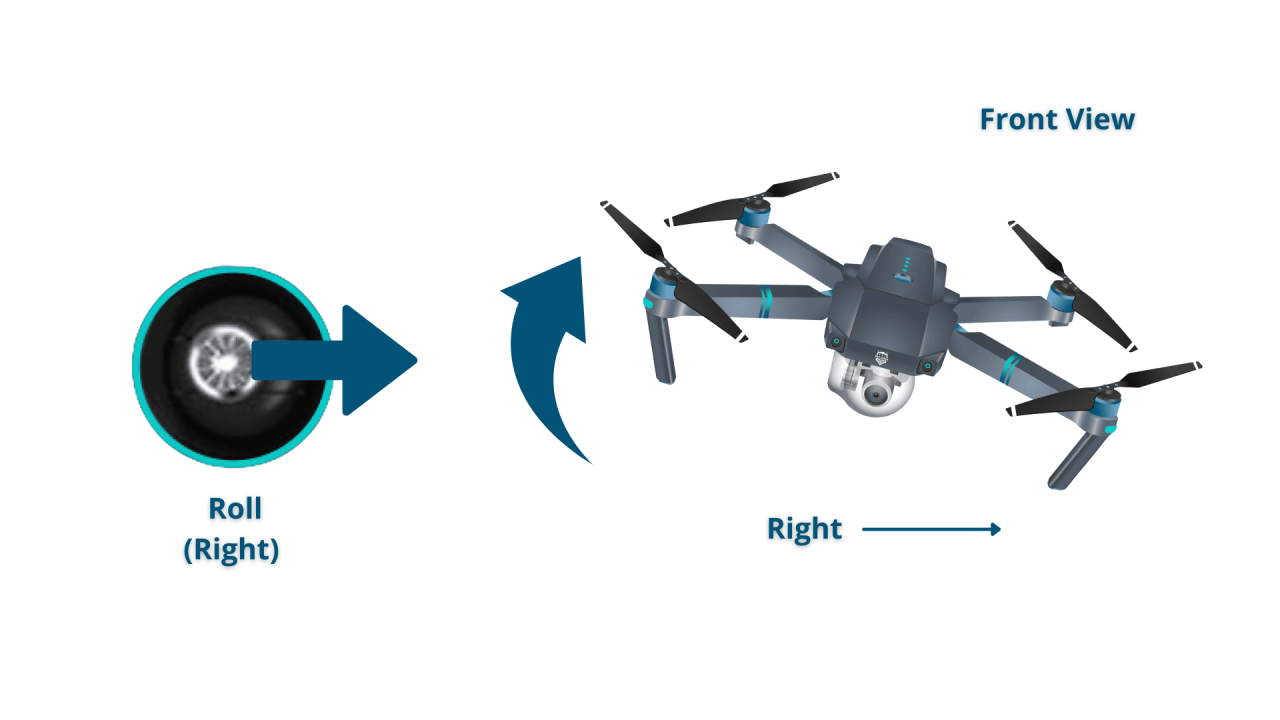
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding drone flight controls is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section describes various flight modes and maneuvers.
Drone Flight Modes
Most drones offer different flight modes to cater to various skill levels and flight situations.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control.
- Sport Mode: Allows for faster speeds and more agile maneuvers.
- Manual Mode: Provides full control over the drone’s movements.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
Drone controls typically involve joysticks or a touchscreen interface. One joystick controls altitude and direction, while the other controls speed and yaw (rotation).
Common Drone Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is fundamental to safe drone operation.
- Taking Off: Gently increase the throttle until the drone lifts off vertically.
- Landing: Slowly decrease the throttle until the drone touches down gently.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady altitude and position.
- Basic Turns: Use the directional controls to smoothly change the drone’s heading.
Drone Control Interfaces
Different drones offer various control interfaces, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Joysticks: Provide precise control and are suitable for experienced pilots.
- Touchscreen: Offer intuitive control, ideal for beginners.
- Mobile App: Convenient for flight planning and camera control.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance

Post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are vital for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation.
Safe Landing and Power Down
Always land the drone gently on a stable surface. Power down the drone and remove the battery.
Drone and Battery Storage

Store the drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Store the battery separately and at a safe temperature.
Common Drone Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and safety.
- Clean propellers and the drone body.
- Check for any physical damage.
- Inspect the battery for any signs of wear or damage.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent problems and ensures safe operation.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection | Before each flight |
| Propeller cleaning | After each flight |
| Battery check | Weekly |
| Full inspection | Monthly |
Advanced Drone Operations and Features
Advanced features enhance drone capabilities, but require a higher level of skill and understanding. This section explores some of these features and potential challenges.
GPS and Return-to-Home (RTH)
GPS enables precise positioning and the RTH function automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point if signal is lost or the battery is low.
Advanced Flight Modes
Advanced flight modes automate certain aspects of flight, such as waypoint navigation and automated flight paths.
Drone Software and Apps
Software and apps provide tools for flight planning, data analysis, and firmware updates.
Challenges in Different Environments
Operating drones in challenging environments requires extra caution and skill.
- Strong winds can affect stability and control.
- Low light conditions can reduce visibility and impair camera performance.
- Rain or snow can damage the drone’s electronics.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. By understanding drone regulations, familiarizing yourself with your drone’s components, and practicing safe flight procedures, you can unlock the immense potential of this technology. Remember that responsible drone piloting not only ensures your safety but also respects the airspace and environment around you. With consistent practice and adherence to safety guidelines, you’ll be capturing stunning aerial footage and exploring new perspectives in no time.
So, grab your controller, plan your flight, and embark on this exciting journey into the world of drones!
FAQ Compilation: How To Operate A Drone
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality. Research models known for their ease of use and consider factors like flight time and camera quality.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the drone model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight mode). Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time; it’s usually between 15-30 minutes.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always fly within visual line of sight and in areas with good signal reception.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and procedures. Registration often involves providing drone details and pilot information.